- Visibility 132 Views
- Downloads 10 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.093
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Ultracentrifugation as a tool for removal of interference caused by lipemia in liver function test
- Author Details:
-
Ajay Rajput
-
Puneet Saxena *
Introduction
The right laboratory test at the right time with the right result leads to quality diagnostics, improved patient care and improved public health around the world.[1] To improve patient outcome, error reduction must receive a great focus in medicine including clinical laboratories. Laboratory test results play a pivotal role in medical decision making and thereby outcome of the patient. Traditionally, only analytical problems are identified as laboratory errors, but now, an extensive scientific literature confirms that it is the extra analytical phase where most errors occur. Pre-analytical errors represent more than half of the total errors which occur in the clinical laboratory.[2],[3],[4] This pre-analytical error can be directly linked to the analytical sample integrity. Hemolysis, hyperbilirubinemia and lipemia of serum can greatly affect the accuracy of many laboratory tests.[5] In clinical biochemistry laboratories, frequently lipemic samples are encountered. Lipemia causes analytical interference in estimation of various biochemical parameters particularly in photometric assays, ion selective electrode (ISE) and immunoassay by light scattering, light absorption, volume displacement, partition between polar and non-polar part or by binding of lipophilic substance to lipoproteins.
Majority of severe lipemia, unlike icterus and hemo lysis, is caused by inherited abnormalities. Other causes of lipemia include alcohol ingestion, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus (DM), metabolic syndrome, h ypothyroidism, pancreatitis, total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and chronic renal failure. Thus, repeat sampling may not always get clear serum because most of the times lipemia is caused by chronic diseases. So, clinical laboratories need to carry out some additional steps of removal of lipemia to minimize the interference caused by lipemia. Removal of lipemia in the same sample can also reduce cost of blood collection containers, needles, phlebotomist payment, patient pain, sample data entry in computers and/or registers, centrifugation time, wear and tear of equipments, analyzer sample positions, technologist payment, waste disposal resources and reporting stationary. Thus, removal of lipemia from same sample can be more practical approach than repeat sampling at other time. To minimize lipemic interference ultracentrifugation, high speed centrifugation, lipid clearing agent or dilution with normal saline can be used. Sample blanking can also be used as an alternative tool.
Lipemia can cause interference by various mechanisms, although not necessarily all mechanism affect all parameters, like light scatter and light absorption causing measurement errors in photometric methods, volume displacement by lipid causing a decreased aqueous phase in indirect ISE methods, partition between polar and non polar phases and b inding of lipophilic compounds and bloc king/masking the binding sites in immunoassay.
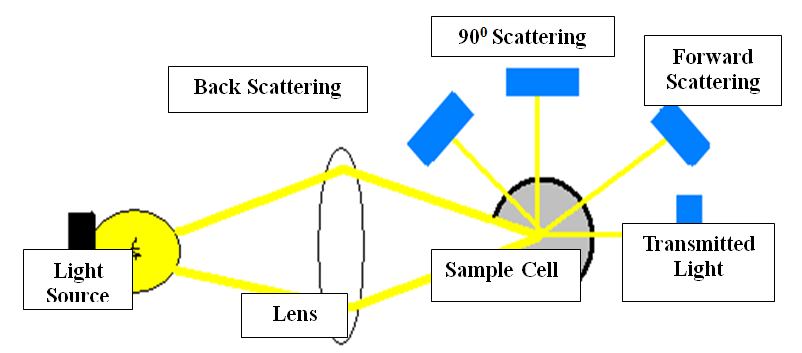
Lipemia causes measurement errors in photometric methods by light scattering and light absorption but extent of the interference depend on the sampling mechanism, lipid composition of the sample and whether the sample is well mixed or not to minimize chylomicrons settling out at the top of the sample.[5],[6],[7] [Figure 1] Sample blanking and bi- chromatic reading decreases the interference but cannot eliminate completely.[5]
Most laboratories measure the concentration of triglycerides and then decide whether the analytical result is valid or not. There is a poor association between the concentration of triglycerides and an assessment of turbidity for visually turbid samples. These decisions are based on assay data sheets provided by manufacturers or are derived from research done using an intravenous lipid emulsion. Concentrations of TG derived from the use of intravenous emulsions cannot be used to extrapolate visually turbid specimens found in clinical practice as it will overestimate the turbidity induced interference.[6] Interference studies for lipemia is difficult to perform because it is difficult to obtain suitable material that mimic lipemic interference unlike hemoglobin or bilirubin. Ideally patient samples are best but difficult to obtain in sufficient quantity for interference studies. To overcome this practical problem Intralipid, a fat emulsion containing soybean oil, egg yolk phospholipids and glycerin is commonly used for interference studies. However, lipids in patient specimens are far more complex than in Intralipid. There is poor correlation between measured turbidity and triglycerides in patient samples because there is nonlinear relationship between triglyceride concentration and sample turbidity in lipemic patient samples.[8] It is due to inhomogeneous nature of lipids in patient samples. Triglyceride is present in various macromolecular forms, like VLDL particles and chylomicrons. Chylomicrons contribute substantially to sample turbidity, whereas VLDL particles make more minor contributions and this distribution is patient specific. Soy-based emulsion Intralipid consists predominantly of small, relatively dense, phospholipid rich liposome and triglyceride rich artificial chylomicrons. Thus use of samples supple mented with Intralipid does not provide a universally applicable method to estimate endogenous assay interference in lipemic patient samples. Thus interference studies should be performed using lipemic patient samples rather than Intralipid supplemented samples.
Interference caused by lipemia can be overcome by, prevention of lipemia, removal of lipemia or change of analytical method. For prevention of lipemia fasting for 8 to 10 hours or stopping of parenteral feeding for 8 hours is advised. For removal of lipemia Ultra-centrifugation for ~15 min, ~20 psi air pressure, and 90,000 rpm, High speed centrifugation at 21.885 x g for 15 minutes, extraction of lipids with organic solvents, precipitation of lipoproteins with polyanions, cyclodextrins, or polyethylene glycol, delipidation with l ipid cle aring agent detergents, lipase or deoxycholate or d ilution of native lipemic sample with normal saline in 1:3 ratio can be used.[6] Alternatively change of method like use of direct ISE instead indirect method can be used.[9]
Ultracentrifugation if available is certainly superior to high speed centrifugation, especially for grossly lipemic samples.[6] High-speed centrifugation at 10,000×g for 15 minutes can be used to remove lipemia in serum, instead of ultracentrifugation.
Aims and Objectives of the study
Identify lipemic samples
Analyze various clinical chemistry analytes in lipemic samples before ultracentrifugation
Analyze various clinical chemistry analytes in lipemic samples after ultracentrifugation
Compare results obtained at objective-3 and objective-4
Materials and Methods
This study was performed in the Biochemistry Section of New Civil Hospital Surat Laboratory Services (NCHSLS), of the New Civil Hospital (NCH), Surat (Gujarat, India) from September 2011 to May 2013. Study proposal was approved by Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC), Government Medical College (GMC) on 2nd of September 2011. This is a tertiary care hospital which receives on an average 200 to 300 samples daily for routine analysis. Among all of these routine samples, we selected the samples which were visibly turbid even after their routine centrifugation at 1,200 x g for 10 minutes. Only samples arriving at Biochemistry Section NCHSLS were included in the study after stripping their identity. Lipemic samples with other interferences like hemolysis oricterus were excluded from the study. From lipemic sample 2 aliquots were prepared each having 500 micro-liter of serum. One aliquot was used to perform all parameters decided to be carried out for study. [Table 1]. Second aliquot was further subjected to the ultracentrifugation at 30000 for 10 minutes at + 4 degree Celsius in a SORVALL Discovery M120 Ultracentrifuge. After which the same biochemical parameters were performed from the infranatant obtained from the ultracentrifuge sample. A total of 50 samples were studied, although some of them were having inadequate serum to perform the biochemical analysis of all the different parameters. In such samples, 2 subsequent samples were mixed to obtain adequate serum quantity. Samples were stored at -40 degree Celsius for not more than 2 weeks to assure quality of samples.
Comparison of results obtained was done by paired Student’s t- test in Microsoft Office 2007. Ratio of (lipemic bias in relation to ultracentrifuge samples) to (Biological Variation, CLIA acceptability criteria and laboratory CV%) was used to find whether the observed difference is clinically significant or not.
| Examination | Principle | Method |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | Para Nitrophenol phosphate AMP 37°C | Kinetic |
| Albumin | Bromocresol Green | End point |
| Alanine Transaminase (ALT) | L-alanine LDH UV Kinetic | Kinetic |
| Total Bilirubin | Diazo with sulphanilic acid in caffine | End point |
| Total protein | Biuret reaction end point | End point |
Method
| Examination | Examination | p' Value | |
| Post-Ultracentrifuged | Pre-Ultracentrifuged | ||
| ALP | 88.80 | 80.90 | 0.0004 |
| ALB | 3.69 | 4.08 | 0.0000 |
| ALT | 17.86 | 32.52 | 0.0000 |
| TBIL | 0.76 | 1.47 | 0.0000 |
| TP | 6.41 | 8.40 | 0.0000 |
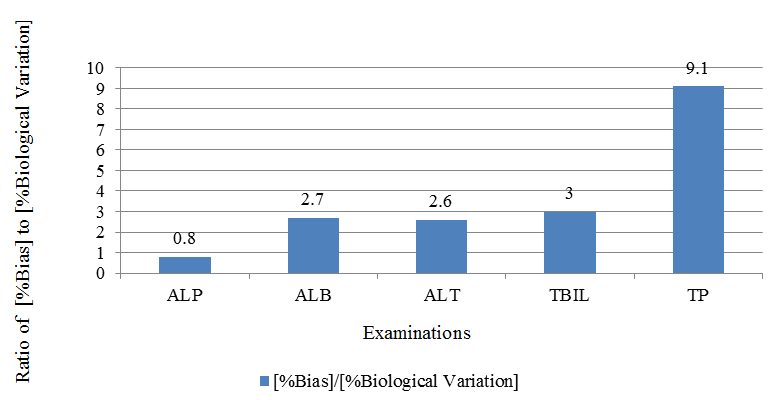
| Examination | % Bias in Lipemic results | % Biological Variation (Source : RIQAS) | [%Bias]/[%Biological Variation] |
| ALP | 9 | 12 | 0.8 |
| ALB | 10 | 4 | 2.7 |
| ALT | 82 | 32 | 2.6 |
| TBIL | 94 | 31 | 3 |
| TP | 31 | 3 | 9.1 |
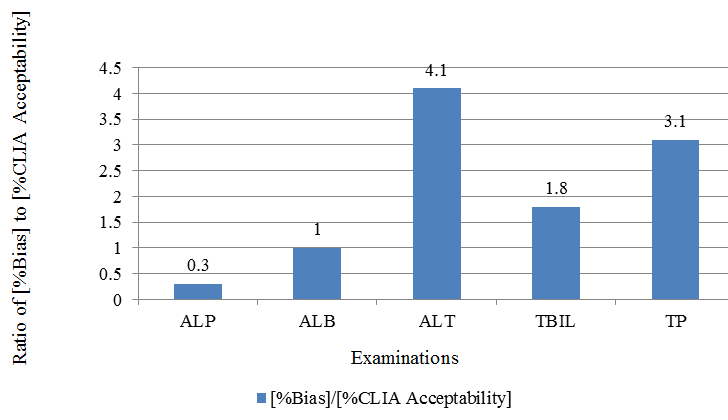
| Examination | % Bias in Lipemic results | % CLIA Acceptability | [%Bias]/[%CLIA Acceptability] |
| ALP | 9 | 30 | 0.3 |
| ALB | 10 | 10 | 1.0 |
| ALT | 82 | 20 | 4.1 |
| TBIL | 94 | 53 | 1.8 |
| TP | 31 | 10 | 3.1 |
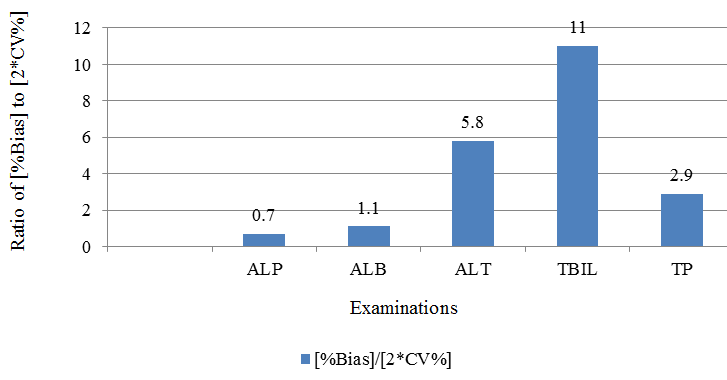
| Examination | Laboratory %CV | 2*CV% (95% probability) | % Bias in Lipemic results | [%Bias]/[2*CV%] |
| ALP | 6.1 | 12.2 | 9 | 0.7 |
| ALB | 4.8 | 9.6 | 11 | 1.1 |
| ALT | 7.1 | 14.2 | 82 | 5.8 |
| TBIL | 4.3 | 8.6 | 95 | 11 |
| TP | 5.4 | 10.8 | 31 | 2.9 |
Results and Discussion
Results of 50 patient samples were analyzed. [Table 2] shows average results of various examinations measured before and after samples were subjected to ultracentrifugation (30000 rpm, 10 minutes, 37000 g).
Paired Student's t-test, comparison with Biological variability, CLIA acceptability criteria, Laboratory CV% were used to find whether interference caused by lipemia was clinically and statistically significant or not. [Table 2].
As shown in [Table 2], the paired student t-test shows statistically significant difference in all parameters between lipemic and ultracentrifuge samples. To understand whether the statistically significant difference is also clinically significant, following ratio were studied.
1. Ratio of % Bias to % Biological variation.
2. Ratio of % Bias to % CLIA acceptability criteria.
3. Ratio of % Bias to % CV of the laboratory.
Such ratio gives idea about whether the observed statistically significant bias is worth consideration in light of laboratory precision, biological variability of the analyte and clinical need for accurate results.
Lipemic interference must be evaluated in light of clinician expectation, rather than relying purely on statistics particularly for an examination with wide biological variation and low clinical need for accurate and precise results.
The obtained average results were compared to find average bias. Calculated %bias was compared to expected %Biological Variation. The Biological variation values were obtained from Randox Internal Quality Assessment Scheme (RIQAS) reports. %Bias= [{average of lipemic samples}/ {average of ultracentrifuge samples}] x 100. [Table 3]. [Figure 2]. As shown in [Figure 2], lipemic interference for ALP is not large enough to warrant clearing of lipemia because intra-individual variation of it is bigger than the bias caused by lipemia. While for some of the examinations, like total bilirubin, total protein, albumin and ALT the bias is very large as compared to biological variability. Hence, for such examinations, removal of lipemia is likely to be clinically useful.
The obtained %bias was compared to expected %CLIA acceptability criteria, [Table 4], [Figure 3] and to twice the %Coefficient of Variance, [Table 5], [Figure 4]. As shown in [Figure 3],[Figure 4], lipemic interferences for total bilirubin, total protein and ALT are large as compared to clinically allowable error as well as compared to intra-laboratory variation. Hence, for such examinations, removal of lipemia is likely to be clinically useful.
Conclusion
Ultracentrifugation results in statistically significant difference in results obtained for all major common clinical chemistry parameters. Clinically significant interference was observed in total bilirubin, total protein and ALT, when difference was considered in the light of biological variation, CLIA acceptability criteria and laboratories imprecision. So, ultracentrifugation can be useful to remove lipemic interference for these parameters.
Source of funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- D Sterry. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. [Presentation] Keystone point of care coordinators meeting; Square, Pennsylvania . 2012. [Google Scholar]
- P Calmarza, J Cordero. Lipemia interferences in routine clinical biochemical tests. Biochemia Med 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- . Governance of preanalytical variability: travelling the right path to the bright side of the moon?. Clin Chim Acta 2009. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P B Szecsi, L Odum. Error tracking in a clinical biochemistry laboratory. Clin Chem Lab Med 2009. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M H Kroll, R J Elin. Interference with clinical laboratory analyses. Clin Chem. Nov 1994. [Google Scholar]
- G Dimeski. Interference testing. Clin Biochem Rev 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Usha Adiga, B N Malawadi. Lipemic index - a tool to measure lipemia. Int J Med Res Rev 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P J Twomey, A C Don-Wauchope, D Mcculloug. Unreliability of triglyceride measurement to predict turbidity induced interference. J Clin Pathol 2003. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J A Bornhorst, R F Roberts, W L Roberts. Assay-Specific Differences in lipemic interference in native and intralipid supplemented samples. Clin Chem 2004. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
