- Visibility 156 Views
- Downloads 13 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.111
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Study of correlation between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and serum creatinine in type 1 diabetes
- Author Details:
-
Muralidhara Krishna C S
-
Jyotsna R *
Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia which is a result of defect in insulin secretion, insulin action or both.[1] Diabetes is a chronic illness that warrants strict maintenance of blood glucose levels, that will otherwise lead to development of complications like nephropathy and retinopathy among others.
DM is the most common non-communicable disease in the world, affecting people across various ages.[2] Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic disorder associated with childhood. Over half the total T1DM population are living in developing nations, and India is the home for an estimated 97,700 children with T1DM.[3]
Diabetic children in India face many challenges that start from non-acceptance by the family, financial hurdles, difficult in accessing medical treatment, lack of awareness in community and so on. It is therefore very important that we as healers sniff out complications in their budding stages and help these children lead better lives.
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a serious chronic complication of diabetes, affecting approximately 20-30% of T1DM patients. It also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease.[4] The most important clinical marker of incipient DN is microalbuminuria.[5] Serum creatinine is another marker that is commonly used to asses renal health.
The term microalbuminuria implies to a small version of the albumin molecule, and not to albumin level that is more than normal but less than the amounts detectable by routine dipstick methods.[6] Microalbuminuria is defined as the appearance of low but abnormal levels of albumin in the urine (30-300mg/24-hour; 20-200 mcg/min; 30-300 mg/g creatinine).[7]
Microalbuminuria is often missed during routine check-ups as the most common method used to detect nephropathy is using dipstick, which detects urinary proteins (>300mg of albumin). Thus microalbuminuria can be measured using the Urinary Albumin Creatinine Ratio (UACR) from a 24hr timed urine sample or random/ spot urine sample.
Measurement of UACR in random or spot urine sample is the best choice for the screening of microalbuminuria in diabetic patients, considering cost and accuracy.[8] Assessing UACR will enable the physician to make changes in management as diabetic nephropathy is potentially reversible.[9]
This study aims to understand the prevalence of microalbuminuria using UACR among the study group and to study the correlation between microalbuminuria and serum creatinine, HbA1c, and random blood sugars.
Materials and Methods
Ethical committee clearance was sought for the study and data collection took place between Jan 2019 – Feb 2019. This is a cross-sectional study involving diabetic children attending OPD at Vani Villas Hospital, Bangalore attached to Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bangalore. Consent was obtained from parents. 30 children were randomly selected; blood samples and urine samples were collected in EDTA and clot activator vacutainer. Children with diagnosed kidney disorders, with fever and any recent infection episode were excluded from the study.
EDTA sample was used to measure HbA1c by latex agglutination inhibition assay. Blood from clot activator vacutainer was allowed to clot, centrifuged, and serum separated. This serum was used to measure Random Blood Sugars by Hexokinase G-6-PDH method, and Serum Creatinine by modified Jaffe’s procedure. All these parameters were analyzed in fully automated Beckman Coulter AU 480.
Spot urine samples were collected. Urinary Albumin by Turbidimetry method and Urinary Creatinine by modified Jaffe’s procedure were analyzed in Abbott autoanalyzer. Urinary albumin creatinine ratio was calculated and expressed in terms of mg/g of creatinine. (ACR is calculated by dividing albumin concentration in milligrams by creatinine concentration in grams and expressed in mg/g).
Data was analyzed in SPSS 21 Version. Kendal tau test was used to assess the correlation of continuous variables that were not normally distributed. Pearson's test was used to assess the strength and significance of the association between continuous variables. The criteria for significance is
P<0.05 is significant; P<0.01 is highly significant; P <0.001 is very highly significant.
Results
This study had 30 patients, comprising of 20 (66%) girls and 10 (33%) boys. The mean ages were 12.8 years in girls and 12.2 years in boys.

This mean duration of diabetes among these children was 4.8 ± 2.4 years. The mean of serum creatinine is 0.49 ± 0.01 mg/ dL, mean of Random Blood Sugars is 263.37 ± 78.99 mg/ dL and that of HbA1c is 10.7 ± 2.58 g%.
| Mean | Std. Deviation | 95% CI | |
| Duration of Diabetes | 4.8 | 2.5 | 3.90-5.69 |
| Serum Creatinine | 0.49 | 0.12 | 0.44-0.53 |
| Random Blood Sugar | 259.4 | 72.25 | 233.54-285.25 |
| HbA1c | 10.7 | 2.58 | 9.77-11.62 |
Urinary albumin creatinine ratio is not normally distributed and expressed in median and IQR as shown below. (After Boot strapping CI for UACR, SE and 95% CI can be calculated)
| UACR | Median | IQR | 25th percentile SE (95% CI) | 75th percentile (95%CI) |
| 11.5 | 29.25 | 5 SE = 1.37 95%CI = (2-8) | 34.25 SE = 11.25 95%CI = (14.25-61) |
In our study group, 21 (70%) children had normal albumin excretion and the remaining 9 (30%) children showed positive microalbum inuria. Among the normal albumin excretion group, the 21 children comprise 14 girls and 7 boys and; the microalbuminuria group had 6 girls and 3 boys.
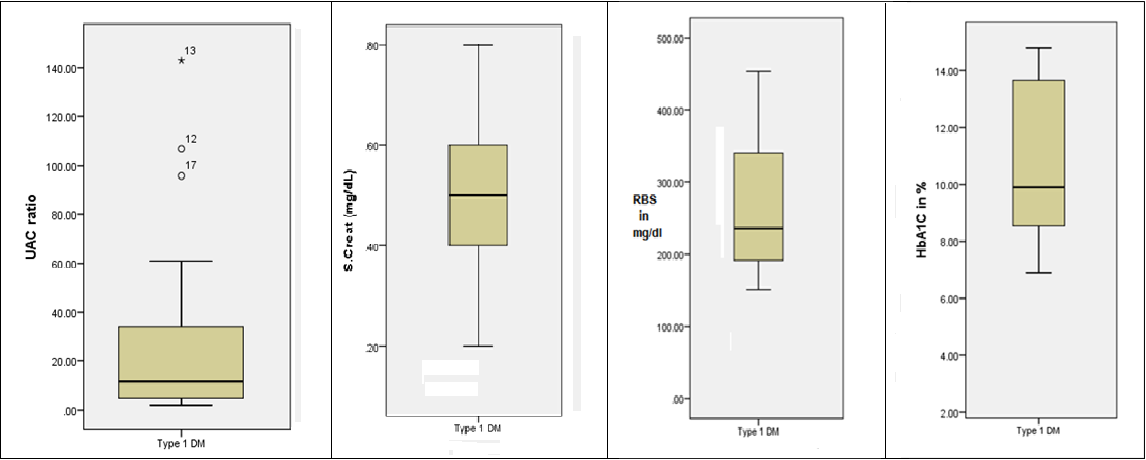
The correlation of UACR with Serum Creatinine, Random Blood Sugars and HbA1c was done using Kendall’s Tau b Corrleataion (an alternative to Pearson’s correlation), to minimise the effect of outliners. UACR correlates with random blood sugars and HbA1c. However there is no correlation between UACR and Serum Creatinine. Correlation is also noted among random blood sugars and HbA1c.
| RBS in mg/dl | UAC Ratio | S.Creat (mg/dL) | HbA 1C in % | |||
| Kendall's tau_b correlation (an alternate to pearson’s) was done to minimize the effect of outliers. | RBS in mg/dl | Correlation Coefficient(r) | 1.000 | .324 * | .084 | .901 ** |
| P Value | . | .013 | .534 | .000 | ||
| N | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| UAC ratio | Correlation Coefficient(r) | .324* | 1.000 | .102 | .303 * | |
| P Value | .013 | . | .470 | .021 | ||
| N | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| S.Creat (mg/dL) | Correlation Coefficient(r) | .084 | .102 | 1.000 | .091 | |
| P Value | .534 | .470 | . | .501 | ||
| N | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| HbA 1C (%) | Correlation Coefficient(r) | .901** | .303 * | .091 | 1.000 | |
| P Value | .000 | .021 | .501 | . | ||
| N | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| Legend: There was a posi tive association of UAC with RBS and HbA1C. There was a pos i tive association of RBS with UACR and HbA1C. There was a pos itive association of HbA1C with RBS and UACR. Abbreviations: HbA1C -Glycated hemoglobin, RBS -Random Blood Sugars, S.Creat -Serum creatinine, UAC-Urine albumin creatinine ratio. *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed); **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). |

Discussion
This study tries to find the correlation of serum creatinine with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio among type 1 diabetic children. There are a handful of longitudinal studies that have followed T1DM patients over years and studied their progression to microalbuminuria and chronic kidney disease. There are not many cross-sectional studies done to measure the prevalence of UACR in a younger population. Also, there were only a few studies that have tried to correlate UACR with serum creatinine in T1DM patients.
Microalbuminuria is defined as 30-300 mg of albumin/g creatinine in urine. In our study group, 9 out of 30, 30% of children showed positive microalbuminuria and the remaining 70%, 21 children had normal albumin excretion.

This study had children living with diabetes since a mean period of 4.8 ± 2.4 years. There are children with diabetes since 10years, having been diagnosed at the ages of 3–4 years and also children with diabetes since 6-7 months, diagnosed at age of 10years. The duration of diabetes too had no correlation with UACR in this study group. It is interesting to note that even children with diabetes less than 2 years had positive microalbuminuria and there were children with diabetes for >5 years but had normal albumin excretion. This finding suggests that UACR does not correlate with the age of onset or with the duration of diabetes. The findings are similar to the conclusions of various studies.[10],[11],[12],[13],[14]
The serum creatinine levels in all the children were found to be within the normal range. This finding suggests that there is no underlying renal damage at the time of testing in these children. By only considering serum creatinine, we infer that no child is suffering from nephropathy.
Correlation of UACR
There is no correlation between serum creatinine and UAC ratio.
There is a positive correlation between UACR and RBS and HbA1c. This is similar to the findings in a study done by Juhi Aggarwal and Mayur Kumar.[15] Increased HbA1c may lead to raised UACR and that in turn can increase the susceptibility to cardiovascular events in the long run.
Conclusion
There is no apparent correlation between UACR and serum creatinine, UACR and age of onset of diabetes or UACR and the duration of diabetes. UACR and Serum creatinine are two independent factors that predict the renal health. Both cannot be used in conjunction while analyzing, but can be used as separate factors.UACR strongly correlates with HbA1c and RBS. When children show high blood sugars and HbA1c, it is suggested to investigate the UACR. This can detect the renal dysfunction in early stages and help in taking appropriate measures in treatment as nephropathy in young is potentially reversible.[9]
Source of funding
None.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- . American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010. [Google Scholar]
- . Diabetes. . [Google Scholar]
- K P Kumar, K Azad, B Zabeen, S Kalra. Type 1 diabetes in children: Fighting for a place under the sun. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R A Cobas, B Santos, P C Da Silva, R Neves, M B Gomes. Progression to microalbuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes: a seven-year prospective study. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2011. [Google Scholar]
- E Sampaio, V D Delfino. Assessing albuminuria in spot morning samples from diabetic patients. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 2008. [Google Scholar]
- C A Burtis, E R Ashwood, D E Bruns. Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics-e-book, 5 Edition Chapter 46.. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- J Redon, J L Rodicio. Microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Hypertens 2004. [Google Scholar]
- J Incerti, T Zelmanovitz, J L Camargo, J L Gross, M J de Azevedo. Evaluation of tests for microalbuminuria screening in patients with diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005. [Google Scholar]
- J L Gross, M J De Azevedo, S P Silveiro, L H Canani, M L Caramori, T Zelmanovitz, T .. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 2005. [Google Scholar]
- A R Andersen, J S Christiansen, J K Andersen, S Kreiner, T Deckert. Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia 1983. [Google Scholar]
- C R Alleyn, L K Volkening, J Wolfson, A Rodriguez-Ventura, J R Wood, L M Laffel. . Occurrence of microalbuminuria in young people with Type 1 diabetes: importance of age and diabetes duration. Diabetic Med 2010. [Google Scholar]
- B A Perkins, L H Ficociello, K H Silva, D M Finkelstein, J H Warram, A S Krolewski. Regression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. New England J Med 2003. [Google Scholar]
- R Amin, B Widmer, A T Prevost, P Schwarze, J Cooper, J Edge. Risk of microalbuminuria and progression to macroalbuminuria in a cohort with childhood onset type 1 diabetes: prospective observational study. BMJ 2008. [Google Scholar]
- B A Perkins, L H Ficociello, B E Ostrander, K H Silva, J Weinberg, J H Warram. Microalbuminuria and the risk for early progressive renal function decline in type 1 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007. [Google Scholar]
- J Aggarwal, M Kumar. Prevalence of microalbuminuria among rural north Indian population with diabetes mellitus and its correlation with glycosylated haemoglobin and smoking. J Clin Diagn Res: JCDR 2014. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
S MKC, R J. Study of correlation between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and serum creatinine in type 1 diabetes [Internet]. Int J Clin Biochem Res. 2025 [cited 2025 Sep 04];6(4):530-534. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.111
APA
S, M. K. C., R, J. (2025). Study of correlation between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and serum creatinine in type 1 diabetes. Int J Clin Biochem Res, 6(4), 530-534. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.111
MLA
S, Muralidhara Krishna C, R, Jyotsna. "Study of correlation between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and serum creatinine in type 1 diabetes." Int J Clin Biochem Res, vol. 6, no. 4, 2025, pp. 530-534. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.111
Chicago
S, M. K. C., R, J.. "Study of correlation between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and serum creatinine in type 1 diabetes." Int J Clin Biochem Res 6, no. 4 (2025): 530-534. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijcbr.2019.111
