Introduction
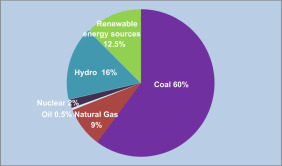
Energy is available on this earth in a number of forms. Some of them maybe immediately used while others require some transformation process. All the developmental activities depend upon energy. Both energy production and utilization are the ultimate measure fora country’s progress. Renewable energy supplies are of ever increasing environmental and economic importance in all countries. Today, in every field the energy demand is increasing. In fact, energy is the basic need for economic, social and cultural development. Sustainable development can be broadly defined as living, producing and consuming in a manner that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It has become a key guiding principle for policy in the 21st century. Therefore, India is looking forward renewable energy and technologies. Energy is regarded as the key factor that lead to sustainable development of any country. Reliable energy supply is essential in all economies for lighting, heating, communications, computers, industrial equipment, transport, etc. In the past few decades energy requirements has steadily increased all over the nations. India’s percapita energy consumption accounts for 37% of the world’s average. India’s energy system is largely based on the use of coal for power generation, oil for transport and industry (Figure 1). India is determined to becoming one of the world’s leading clean energy producers. The Government of India has already made several provisions and established many agencies that will help it to achieve its goal. Renewable energy offers our planet a chance to reduce carbon emissions. The detrimental environmental effects of burning the fossil fuels imply that current patterns of use are unsustainable in the longer term. In particular, CO2 emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels have significantly raised the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere and it will enhance the greenhouse effect and lead to significant climate change. In short, renewable energy supplies are more compatible with sustainable development than are fossil fuels in regard to both resource limitations and environmental impacts.
Renewable Energy in India
India’s population is growing at an annual rate of 1.6%. It is true fact that, fossil fuel energy becomes unavailable in near future, India may face energy shortages significantly due to increase in energy cost and energy insecurity. Increasing use of fossil fuels also leads to environmental problems. To overcome energy shortage the renewable energy sources can be used. Renewable energy1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 is a clean and sustainable source of energy derived from nature and it has potential to provide solutions to the vulnerable energy problems being faced in India. India is the only country in the world to have renewable energy development, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy which has launched one of the world’s largest programs on renewable energy. Despite the progress in renewables’ adoption, it is insufficient to achieve the Sustainable Development Goal 7 within the deadline. This is because of the fossil fuel usage causes to climate change.
Current Scenario of Renewable Energy in India
India has become the fourth largest energy consumer in the world after the USA, China and Russia. The renewable energy sector in India has emerged as a significant context especially affecting the power generation capacity. This supports the government’s agenda of sustainable development while becoming an integral part in meeting the nation’s energy needs. The largest renewable capacity expansion programme in the world is being taken up by India. The Indian Government has taken several initiatives since 2010 such as introduction of the concept of solar parks, launching of a massive grid connected rooftop solar panel and solar pump scheme with a target of installing 120,000 solar pumps and programme to train 1 lakh people for solar installations under the Surya Mitra scheme.The other significant initiatives are launching of improved cook stoves, effective research and development activities in solar, biofuels, hydrogen energy and fuel cells, etc.
Future Renewable Energy Targets in India
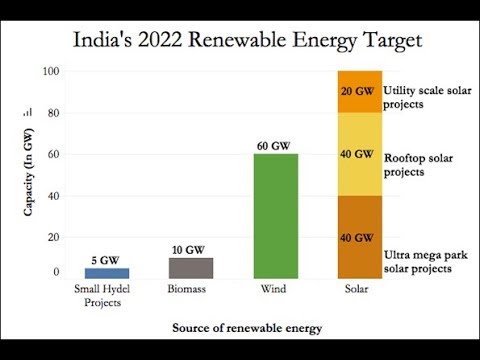
The twin challenges facing in India on energy and environmental. India expected to work towards increasing the role of renewable in the future energy systems. Renewable energy technologies change with technological and commercial status. India with large renewable energy sources is to set to have large scale development and deployment of projects. India is the fifth largest producer of solar energy and the sixth largest producer of renewable energy. The Government focus the target of renewable energy capacity to 175GW by the year 2025 which includes100 GW from solar, 60 GW from wind,10 GW from bio-fuel and 10 GW from hydropower (Figure 3). With this target, India will become one of the largest Green Energy utilizer in the world, surpassing several developed countries. Government of India in its submission to the United Nations Framework Convention on climate change on Intended Nationally Determined Contribution has stated that India will achieve 50% cumulative Electric power capacity from nonfossil fuel based energy resources by 2030.
Conclusion
Energy security, economic growth and environment protection are essential for sustainable development fora cleaner, greener and safer place for our future generation of any country. The need to appreciate the efforts for further sustainable development and promotion of renewable energy sources has been felt in India. Finally, renewable energy offers enormous benefits for the future. India has plenty of renewable energy potential to bridge the gap between supply and demand. Electric and Hydrogen fuel based vehicles are the most suitable options for moving towards progress. If this is achieved then the limitations of the clean energy sources can be easily overcome.